What is a Class B IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a numerical identifier allocated to each device that connects to a network, facilitating communication across the internet. These addresses are generally categorized into five primary classes: A, B, C, D, and E. Each class is designated for particular functions, with Class B being widely utilized for medium to large-scale networks. In this article, we will thoroughly examine Class B IP addresses, focusing on their structure, importance, and various applications.
Table of Contents
ToggleStructure of a Class B IP Address
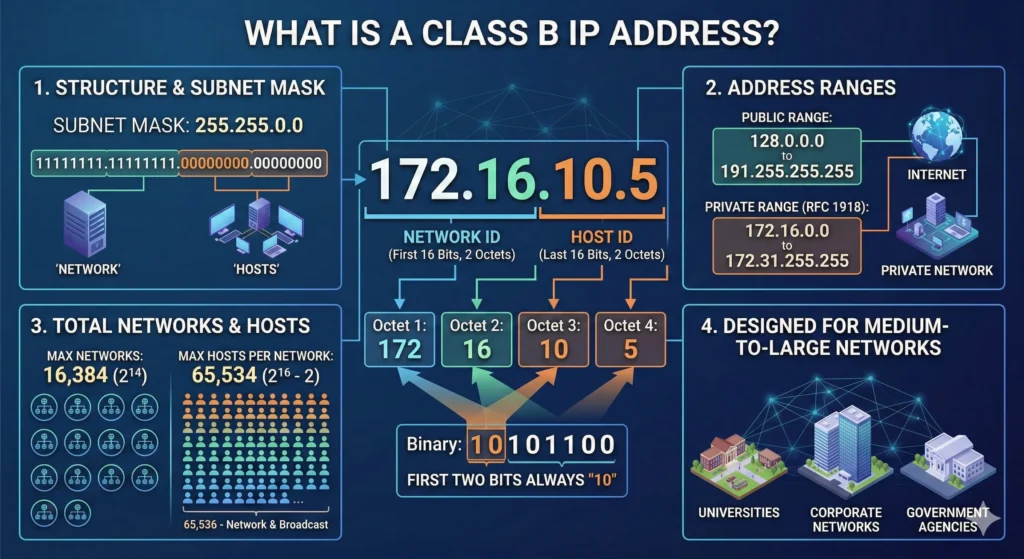
A Class B IP address is defined by its first octet, which ranges from 128 to 191. An IP address consists of four octets, each separated by a dot, such as 172.16.0.1. For a Class B address:
The first two octets represent the network portion (Network ID).
The last two octets are designated for the host portion (Host ID).
This setup strikes a balance between the size of the network and its scalability, rendering it suitable for organizations that need a moderate quantity of devices within their network.
Subnet Mask for Class B
To establish the limits of a Class B IP address, the standard subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 is applied. This mask signifies that the initial two octets are designated for the network, whereas the last two octets are available for allocating distinct addresses to devices.
Number of Available Addresses
Class B IP addresses offer a substantial range for device allocation:
Total networks: 16,384
Hosts per network: 65,534
A Class B network has the capacity to support thousands of devices, rendering it an appropriate option for medium-sized businesses, educational institutions, or governmental entities.
Private vs. Public Class B IP Addresses
Not all Class B IP addresses are available for public internet access. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has allocated a portion of these addresses specifically for private network use. The private range for Class B addresses extends from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255, which is commonly used for internal networking in numerous organizations.
For public networks, Class B IP addresses that fall outside this private range are employed. These addresses are distinct across the internet, facilitating uninterrupted global communication.Benefits of Class B IP Addresses
Scalability: With the ability to host thousands of devices, Class B is ideal for organizations planning to expand their networks.
Flexibility: The division between network and host bits allows for efficient subnetting, enabling better utilization of available IPs.
Private Addressing: Organizations can use private Class B IP ranges to avoid conflicts on the public internet and enhance security.
Use Cases of Class B IP Addresses
Class B IP addresses are widely used in environments that require more addresses than Class C can provide but fewer than Class A:
Educational Institutions: Universities and colleges often use Class B networks to manage multiple departments and student networks.
Corporate Networks: Medium to large enterprises utilize these IPs for employee systems, internal servers, and IoT devices.
Government Agencies: Class B ranges are well-suited for municipal or state-level networks.
Also Read: Why Use a Class B IP Address?
Also Read: What is a Class C IP Address?
Conclusion
Comprehending Class B IP addresses is crucial for network administrators and IT professionals involved in the design and management of IP-based systems. These addresses offer a favorable equilibrium between capacity and manageability, making them suitable for organizations with moderate networking demands.
If you are intending to establish a network or enhance an existing one, it is advisable to evaluate whether a Class B IP address range meets your requirements. Thoughtful planning guarantees uninterrupted connectivity and optimal utilization of IP resources.



